
What does Barracuda’s recent report reveal about web application security? (Source – Shutterstock).
Are your web applications secure? Barracuda reports high incident and breach involvement
- Barracuda’s report highlights a significant increase in cyberattacks targeting web applications.
- Barracuda’s 2023 analysis shows over 18 billion attacks on applications.
- The report underscores the critical need for advanced cybersecurity measures against rising web application attacks.
Barracuda, a provider of cloud-first security solutions, has released its latest Threat Spotlight report. The report emphasizes the increasing trend of cyberattackers exploiting vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in web applications to access and extract valuable data.
In 2023, Barracuda successfully countered over 18 billion attacks targeting various web applications, with 1.716 billion occurring in December alone. The report offers an in-depth analysis of these incidents, particularly those identified by the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP), highlighting the critical challenges Barracuda Application Security faces.

Web applications vulnerabilities and misconfigurations are being exploited. (Source – Barracuda).
The growing target: web applications in the cybersecurity crosshairs
Web applications, which are pieces of software accessed through web browsers and include popular tools such as Microsoft 365, Google Docs, and Gmail, have become a significant focus for cyberattacks. This is supported by Verizon’s Data Breach Investigation Report (DBIR), which indicates that web apps were involved in 80% of all security incidents and 60% of breaches in 2023.
The Threat Spotlight by Barracuda reveals that a significant portion of attacks on web applications are aimed at exploiting security misconfigurations, including coding and implementation errors, which account for 30% of the incidents. Moreover, 21% of these attacks involved code injection, where harmful code is inserted and executed by the application. These attacks are not limited to SQL injections but also include Log4Shell and LDAP injections, often used in managing privileges like Single Sign-On (SSO) functionalities.
Barracuda’s analysis also shows that bot attacks on web applications were prevalent in 2023. Its data indicates that in December 2023 alone, 53% of bot attacks on web applications consisted of volumetric distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
These volumetric DDoS attacks, typically launched by large botnets comprising connected IoT devices, employ brute force to overwhelm the target with excessive data packets, consuming bandwidth and resources. It’s important to note that such attacks can also serve as a distraction for more targeted and severe attacks on the network.
Additionally, the data reveals that approximately one-third (34%) of bot attacks in December were application DDoS attacks, focusing on specific applications, while 5% were attempts to take over accounts using bots.
Barracuda utilizes machine learning and its Privileged Account Protection feature to detect account takeover attacks. This protection analyzes login patterns to identify anomalies and alerts security administrators to any unusual activities, potentially indicative of an attack, preventing incidents in their early stages.
The continuous exploitation of vulnerabilities, especially in older and outdated application components, presents ongoing challenges. For instance, the ProxyShell vulnerabilities, first identified in 2021, have been repeatedly exploited, leading to numerous high-profile breaches, including ransomware attacks.
Additionally, threat actors occasionally target less prominent but still dangerous vulnerabilities. An example is the Androxgh0st malware, which prompted a warning from the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) on January 16, 2024.
Barracuda’s analysis of common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs) reveals significant probing of their installations in recent months. The scanning patterns for these vulnerabilities, which started simultaneously and peaked similarly, suggest a coordinated or singular attack campaign.
Notable CVEs include CVE-2017-9814, a high severity (7.5) vulnerability enabling denial-of-service attacks, and CVE-2018-151333, a severe (8.1) remote code execution vulnerability in the Laravel framework. Both vulnerabilities were modified in 2023. Another is CVE-2021-41773, a high-severity (7.5) Apache HTTP server vulnerability that changed in 2023.
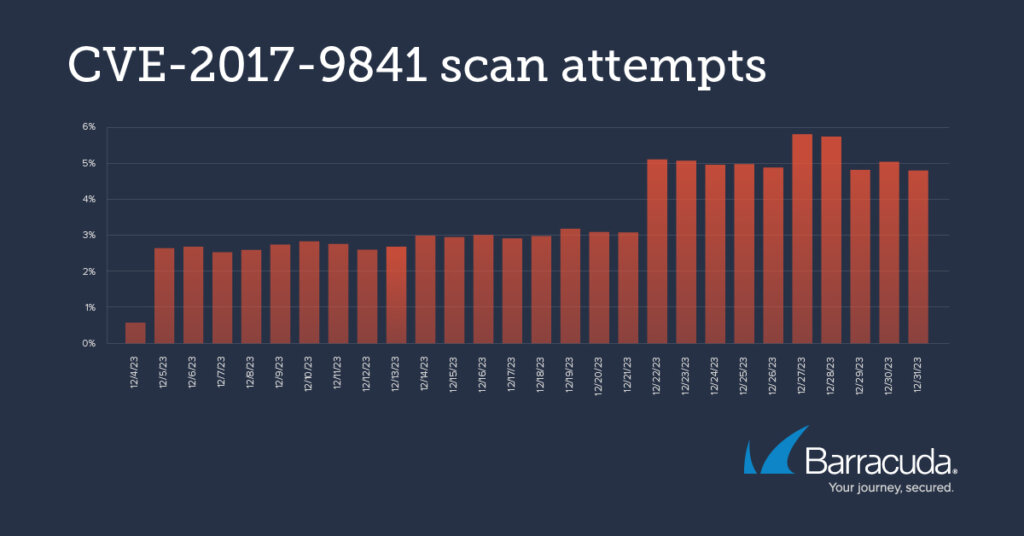
CVE-2017-9814 is a high severity (7.5) vulnerability. (Source – Barracuda).
The report also examines the geographical origins of these scans, noting a significant number of blocked Tor IPs and a high proportion of scans from the US. This is likely reflective of the attacks originating from publicly accessible US servers. The regional distribution of these scans has also varied over time, with Tor being a top source region in early December before dropping off, likely due to comprehensive blocking measures.
Defending the digital frontier: Barracuda’s expert insights
Tushar Richabadas, principal product manager of application security at Barracuda, commented on the increasing attacks on web applications and APIs, noting the challenges defenders face in keeping up with both new and old vulnerabilities. The software supply chain for critical applications, as exemplified by the Log4Shell vulnerability, can also contain flaws.
Richabadas emphasized that attackers often exploit older vulnerabilities that security teams may have overlooked, aiming to breach unpatched applications and infiltrate networks. He underscored the importance of organizations remaining vigilant, constantly updating their security measures, and addressing new and longstanding vulnerabilities to protect against sophisticated cyberthreats.
This continual vigilance and updating of security protocols are essential in safeguarding against the intricate methods employed by cybercriminals. As Richabadas pointed out, the dynamic nature of cyberthreats requires a proactive and comprehensive approach to security. This involves not only addressing new vulnerabilities as they arise but also revisiting and reinforcing defenses against older vulnerabilities that may have fallen out of immediate focus but still pose a significant risk.
By understanding the latest attack trends, implementing advanced security solutions, and maintaining an ongoing commitment to cybersecurity awareness and education, businesses can better protect their web applications and, by extension, their valuable data and digital infrastructure from the growing threats in the digital world.
READ MORE
- 3 Steps to Successfully Automate Copilot for Microsoft 365 Implementation
- Trustworthy AI – the Promise of Enterprise-Friendly Generative Machine Learning with Dell and NVIDIA
- Strategies for Democratizing GenAI
- The criticality of endpoint management in cybersecurity and operations
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications




