
Users can now buy and sell specialized chatbots at the OpenAI GPT Store. (Photo by Kirill KUDRYAVTSEV / AFP)
You can now buy chatbots at the OpenAI GPT Store
- GPT Store is a chatbot LLM marketplace launched by OpenAI.
- Users can buy and sell chatbots, with a revenue paid to users as well.
- Over three million custom versions of ChatGPT have been created since GPTs were announced.
Users can now buy and sell specialized chatbots at the OpenAI GPT Store. The marketplace was recently launched by OpenAI to let users get more access to chatbots, and also showcase their developments based on the company’s language models.
According to a blog post by OpenAI, the store features a diverse range of GPTs developed by partners and the community. Users will browse popular and trending GPTs on the community leaderboard, with categories like DALL·E, writing, research, programming, education, and lifestyle.
Since announcing GPTs, OpenAI says that users have created over three million custom versions of ChatGPT. Many builders have also shared their GPTs for others to use. OpenAI is making the GPT Store available to ChatGPT Plus, Team and Enterprise users.
OpenAI will also highlight useful and impactful GPTs every week. At its launch, the company featured the following GPTs:
- Personalized trail recommendations from AllTrails
- Search and synthesize results from 200M academic papers with Consensus
- Expand your coding skills with Khan Academy’s Code Tutor
- Design presentations or social posts with Canva
- Find your next read with Books
- Learn math and science anytime, anywhere with the CK-12 Flexi AI tutor
Apart from the GPT Store, OpenAI also unveiled ChatGPT teams.
Can builders benefit from OpenAI GPT Store?
Given that the GPT Store is a marketplace, builders can also look to make some profit from the GPTs they sell on the platform. OpenAI added that it will launch a GPT builder revenue program in the first quarter of 2024. However, the revenue program will only be available to US builders for now. They will be paid based on user engagement with their GPTs.
While building a GPT is simple, to share a developed GPT in the store, builders will need to save their GPT for everyone. They would also need to verify their builder profile on the platform.
On concerns of copyright, OpenAI states that they’ve established a new review system in addition to the existing safety measures they’ve built into their products. The review process includes both human and automated reviews. Users will also be able to report GPTs that do not meet policies, brand guidelines or are not GPT compliant.
Chelsea Alves, a consultant at UNmiss shared with Tech Wire Asia, “This initiative not only propels the ever-growing field of artificial intelligence forward but also empowers creators to turn their hard work into a rewarding effort. The democratization of AI through the OpenAI ChatGPT Store becomes more beneficial for creators to be recognized and fairly financially compensated for their contributions.”
Alves pointed out that a sticking point with AI-content generation has long been its use of existing content as well as how that derails the authenticity and hard work put in by the original content creator.
“The OpenAI ChatGPT Store addresses this concern by creating a platform where creators are not only acknowledged for their efforts but also benefit through financial means. This innovative marketplace facilitates a fairer compensation model that will likely, in turn, prompt creators to get even more creative to reap the advantages,” added Alves.
Getting started on the store will vary in difficulty depending on the complexity of the GPT. In a Reddit discussion, one user states, “From the basic end if you can articulate well and upload knowledge files, you can get one going in a short time. If you want to connect with outside APIs there is a bit more you will need to know, but there are resources are out there to learn about this.”
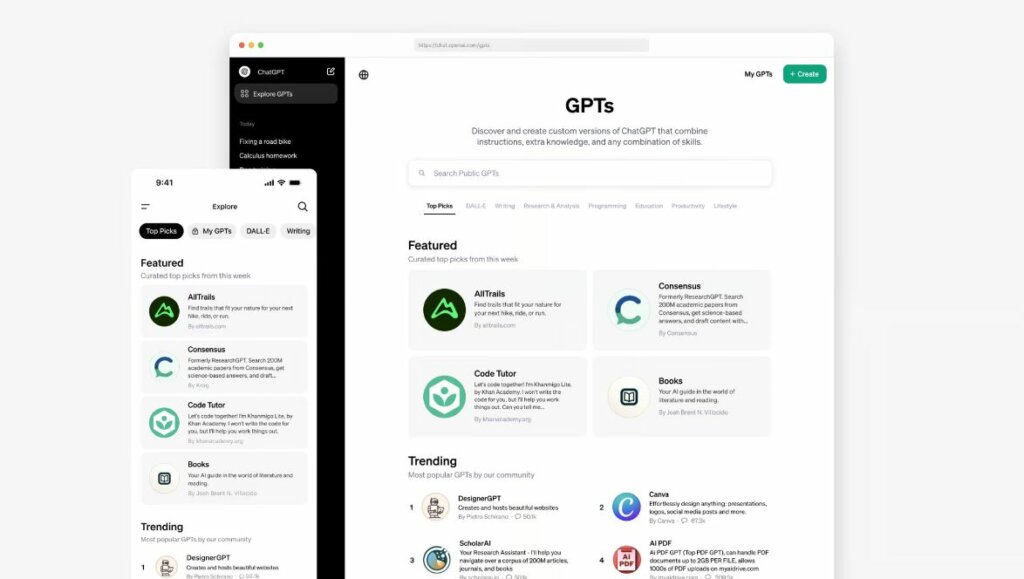
Over 3M GPTs have been created and now you can find the most useful versions of ChatGPT for you. (Source – OpenAI).
Will there be regulatory and security concerns?
While OpenAI will have a review system on the GPTs, Jamie Moles, senior technical manager at ExtraHop, believes that there will be less moderation on the platform than on other stores.
“There is clearly less moderation when it’s bespoke, as you can define your own ‘rules of engagement’ for the GPT you build. When you create the bot, it specifically asks “Also, are there any specific topics or types of advice that should be avoided?” allowing the creator – who might be publishing the bot to the public – to limit the scope of the bots’ replies. This is a mild form of the limitations put on the main ChatGPT program by OpenAI,” said Moles.
Moles also pointed out that he was surprised that the bespoke GPT allowed for access to exploit code creation, for example, which has been limited in the past.
“In reality, if a clever user breaks down the various components of a piece of malware, it is feasible that you could get ChatGPT to write code for those individual components and then pull them all together yourself to get a functioning program,” added Moles.
Moles had conducted his own experiments with the ChatGPT builder to create a “Cyber Sentinel” that writes phishing emails and Python code to exploit EternalBlue and create reverse shells for remote access to machines. Eternal Blue is a popular exploit used by bad actors like the global WannaCry Ransomware attacks.
“In the hands of a cybercriminal, this could very easily be exploited and misused to a mass degree. Perhaps even scarier, you don’t need to be a cybercriminal to be able to do this,” said Moles.
READ MORE
- 3 Steps to Successfully Automate Copilot for Microsoft 365 Implementation
- Trustworthy AI – the Promise of Enterprise-Friendly Generative Machine Learning with Dell and NVIDIA
- Strategies for Democratizing GenAI
- The criticality of endpoint management in cybersecurity and operations
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications




