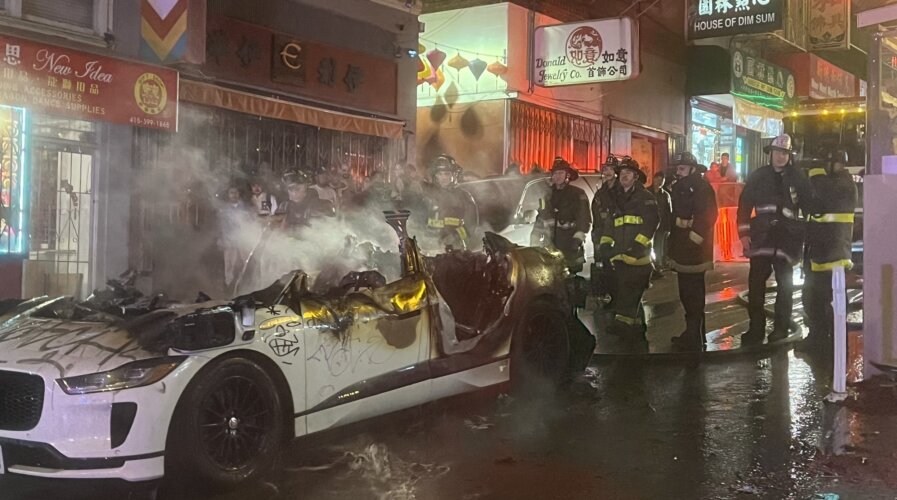

A crowd had vandalized a Waymo driverless tax. (Image source – X)
Self-driving vehicles under fire
- Self-driving vehicles face challenges from regulators and road users.
- There have been several incidents involving the vehicles.
- Google Waymo set on fire by a crowd in San Francisco
Self-driving vehicles operate without human input, using sensors, cameras, computers, and algorithms to perceive the environment, monitor systems, and control the vehicle. They vary in the level of automation, from partially assisting a human driver to fully replacing them.
Self-driving vehicles have the potential to improve the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of transportation, but they also face many technical, ethical, and regulatory challenges. Challenges need to be addressed by the industry so all road users will feel safe using and being around the vehicles.
Over the past few years, regulations for autonomous vehicles on public roads have been the subject of much debate. While there has been more acceptance of the self-driving vehicles on public roads, there are still those who are concerned about the risks the vehicles pose, especially when it comes to the safety of the public and passengers.
Self-driving vehicles are a rapidly developing technology that is subject to different regulations across US states. According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, 29 states and Washington D.C. have enacted legislation related to autonomous vehicles. The US Department of Transportation and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration also provide federal guidelines and recommendations for the testing and deployment of self-driving cars.
However, the rules vary on aspects such as the definition of vehicle operator, the presence of a safety driver, the level of automation, and the data recording and reporting requirements. In March 2022, the US government cleared the way for driverless vehicles without steering wheels or pedals, as long as vehicles met other safety standards. Therefore, self-driving cars are allowed in the US, but with different conditions and limitations placed on them, depending on the state and the type of vehicle.
The same types of rules apply to self-driving cars in every country. China, which has already legalized the use of robotaxis, has set various conditions and limitations that similarly depend on the level of automation and the purpose of the vehicle.
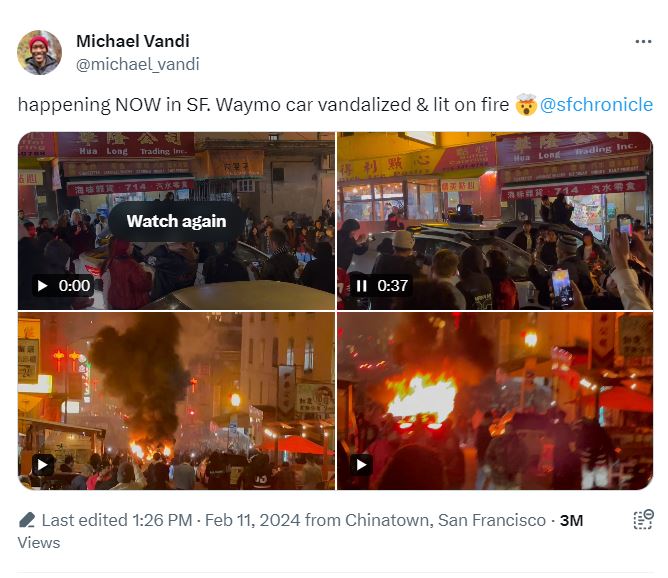
The fire takes place against the backdrop of simmering tension between San Francisco residents and automated vehicle operators.
Incidents involving self-driving vehicles
There are five levels categorizing autonomous vehicles that are generally accepted by the industry worldwide. Level 4 and 5 self-driving vehicles need no human intervention to operate, with technology controlling the vehicle. However, accidents involving these vehicles always cause concern.
There have been several incidents involving self-driving vehicles recently in the US. While some of them have been minor, there have also been several more severe accidents in which passengers or road users were badly injured or lost their lives.
Recently, a Google Waymo self-driving vehicle was involved in an accident in San Francisco. In that instance, an autonomous vehicle struck a cyclist who had reportedly been following behind a truck that was turning across its path.
Last year, the California DMV suspended Cruise’s robotaxi operations. In one incident, a robotaxi struck and dragged a pedestrian along the road for several meters. Prior to that, there have been reports of self-driving cars causing traffic snarlups or crashing into other vehicles.
More recently, a crowd vandalized a Waymo driverless taxi. According to a report by The Verge,one person jumped on the hood of the vehicle and smashed its windshield. A crowd applauded the incident before surrounding the vehicle and breaking its windows, vandalizing it and eventually setting it on fire.
There have been no reports pinpointing the exact motive for the incident. A Waymo representative told The Verge that the autonomous car “was not transporting any riders” when it was attacked. Fireworks were alledgedly tossed inside the car, causing the blaze.
The incident is most likely the first major incident involving a crowd vandalizing a self-driving vehicle.

A Waymo autonomous vehicle on Market Street in San Francisco, on November 17, 2023. (Photo by Jason Henry / AFP)
Can more regulations solve the problem?
The latest incident in San Francisco represents a wake-up call for operators and legislators. There is no denying that the public is still not convinced about the safety of fully-autonomous vehicles.
According to a report by Reuters, California lawmakers and labor unions rallied to call for laws to oulaw autonomous trucks without human drivers, amid rising safety concerns arising from accidents involving self-driving taxis from General Motors and Alphabet. California state lawmakers are pushing for stricter control through two bills of proposed legislation.
“Those accidents have put an exclamation point on the need for legislation,” Senator Dave Cortese said. Cortese is the sponsor of a bill that would give cities control over issuing permits for autonomous vehicles (AV), plus the ability to enforceme AV-specific laws. The second proposed bill requires a trained human driver to be present behind the wheel of any self-driving vehicle weighing more than 10,001 pounds, a classification that includes commercial trucks.
While these regulations involve self-driving commercial vehicles, they could also have an impact on how self-driving cars are operated and managed in the future.
“It’s a common-sense measure that keeps humans on board a truck until we have a plan for our workers and we’re sure that tech bros aren’t jamming unsafe technology down our throats,” State Assembly member Cecilia Aguiar-Curry said.
READ MORE
- 3 Steps to Successfully Automate Copilot for Microsoft 365 Implementation
- Trustworthy AI – the Promise of Enterprise-Friendly Generative Machine Learning with Dell and NVIDIA
- Strategies for Democratizing GenAI
- The criticality of endpoint management in cybersecurity and operations
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications




