
Insurance everywhere all at once: the digital transformation of the APAC insurance industry

Insurance has never been a stagnant industry, however the current era is proving to be one of unprecedented change. With the rise of digitalization, changing customer expectations, and the emergence of new business models like embedded insurance, the insurance landscape is evolving at an accelerated pace. Insurers must urgently address their technology infrastructure and adopt an open technology strategy as consumers demand seamless experiences and personalized products. This means embracing cloud technology, leveraging AI and data analytics, and forming strategic partnerships to stay competitive. The stakes are high, and the time to act is now. Failure to do so could result in irrelevance and loss of market share in an industry that is rapidly transforming.
The current state of the insurance industry
TechWireAsia spoke to Nikola Djokic, the Managing Director of Insurance at SAP Fioneer, about the current state of the insurance industry and the challenges it faces. “Insurance is undergoing a revolution,” he said. “The rise of the insurtech and access to data has allowed non-insurance brands to enter the market and offer insurance as part of their offering, adding value to their customers and generating new revenue. Rather than a separate vertical industry, insurance is now taking a role in several ecosystems. This all represents significant new market opportunities for insurtechs, new players and incumbents alike, but the change is rapid, and traditional insurers need to adapt quickly to take advantage of and benefit from the new world order.”
Digitalization has traditionally been hampered in insurance due to legacy systems. Often built over decades, they have created data silos and operational inefficiencies that hinder the adoption of modern technology. Insurers have struggled to integrate new digital solutions seamlessly into their existing infrastructure, leading to fragmented customer experiences and slow response times. Moreover, the risk-averse nature of the insurance industry has contributed to a reluctance to invest in digital transformation initiatives. Insurers have been cautious about migrating sensitive data to the cloud and adopting emerging technologies like AI and machine learning due to concerns about data security, regulatory compliance, and the potential for disruption to established business processes.
Mr Djokic said: “Decisions need to run from the user interface through the middle office to the back office and back again, and these have typically been disconnected. The process of assessing a customer for a policy, or a claim for a payment, traditionally required (and in many cases still requires) a lot of manual intervention.”
Third-party data has been available to facilitate these assessments, but it is rarely integrated into the core insurance solution, making it challenging to meet customer expectations for digital immediacy. “This has allowed new players – neo-insurers – unencumbered by legacy systems or processes to leapfrog ahead in niche areas,” said Mr Djokic.
Insurance penetration in Asia, standing at around two percent in developed markets and one percent in emerging markets, presents a barrier to sector expansion despite the region’s vast population of over four billion people. TechWireAsia caught up with Chirag Shah, the Managing Director of JAPAC Digital and Core Insurance at SAP Fioneer, to try and understand the growth potential of the industry in APAC.
He said: “The Asia Pacific insurance market is experiencing shifts driven by post-COVID-19 customer perceptions, particularly in healthcare. Rising awareness of the protection gap has led to increased demand for health and life insurance products, especially in emerging markets, where insurance penetration and density are lower compared to developed markets.
“Insurers must navigate challenges such as mobility, cybersecurity, and climate change while enhancing value creation within existing operations like claims and underwriting. Challenges include slowing growth, low penetration, and rising combined ratios, particularly in emerging markets.”
Insurance everywhere
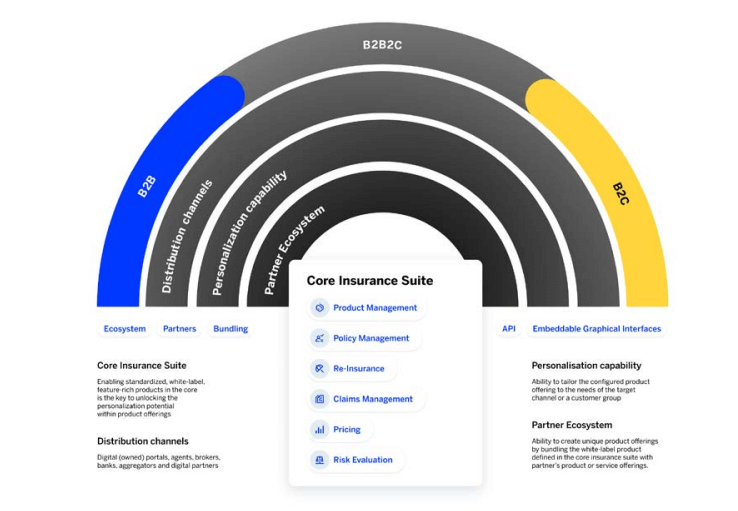
Source: SAP Fioneer
“‘Insurance everywhere’ alludes to embedded insurance,” said Mr Djokic. “Delivering insurance at the point it’s needed, as part of a purchase process, circumventing the need for a consumer or business purchaser to undertake a separate set of steps to insure their car, home, electronic item, or holiday.” By making insurance products more accessible and convenient, insurers can reach a broader audience and meet the evolving needs of modern consumers. Accessibility also opens up new opportunities for insurers to partner with other industries and platforms, expanding their reach and market presence.
Mr Djokic added: “[It] has the potential to increase the level of insurance generally, which is good news not just for the industry but society as a whole, as it becomes more protected. But it also means that non-insurance companies can take market share from the traditional players, unless those players turn the situation to their advantage, and become the ones offering insurance solutions to new industries.”
Personalization with data and AI
Traditional insurance practices rely on limited data and broad assumptions, often leading to unfair assessments of risk based on general demographics. This has sparked frustration among consumers who feel penalized for careful behavior while subsidizing riskier individuals. However, emerging technologies like telematics and IoT devices are beginning to change this dynamic by allowing personalized assessments and rewards for behaviors like safe driving and healthy lifestyles.
“We have seen examples of health insurance companies monitoring exercise levels with fitness trackers and dropping premiums accordingly,” said Mr Djokic. “There is now more data accessible to the insurer to contribute to the risk assessment, be it social media or online behavioral data, credit scores or – in the case of embedded insurance – data held or gathered by the non-insurance company.
“For the first time, we’re witnessing a ‘win-win’ in the industry, where data helps the insurer reduce their risks and pass this on in the form of reduced premiums to the customer. As consumers become accustomed to this level of tailoring, it will be essential for insurers to offer personalized insurance to stay competitive.”
Increased data availability is enhanced by AI, particularly machine learning, enabling dynamic risk assessments and tailored policy generation. Predictive analysis and risk scenario modeling help insurers proactively cover emerging risks like climate change and technological advancements. Automated policy drafting and scenario simulation improve efficiency and ensure comprehensive coverage tailored to specific customer needs.
“AI can interpret data accurately and immediately to deliver real-time claims processing and payment while mitigating risks.” Said Mr Djokic. “It delivers the speed consumers and businesses now expect while protecting the insurer.”
Mr Shah added: “Insurers in Japan and Korea may leverage AI and data analytics uniquely to cater to their distinct demographics and technological landscapes. Japan’s aging population may drive insurers to develop AI solutions for personalized services and risk management tailored to older demographics. Korea’s advanced technological infrastructure may facilitate the adoption of AI-driven underwriting and pricing models to enhance customer experiences and operational efficiency.”
The future with SAP Fioneer
On the future of insurance in APAC, Mr Shah said: “Despite challenges, Asia remains an attractive insurance market, with emerging markets expected to see higher premium growth in the next two years driven by rising economic growth, increasing risk awareness post-pandemic, and digitalization of distribution channels.
“Digitally embedded insurance is expected to grow significantly by 2030, driven by increasing digital penetration and partnerships with digital ecosystems.”
Mr Djokic says that the key to taking advantage of the new opportunities in insurance is connectivity – the ability to connect a core insurance solution to, for example, a new data source or user interface. “The secret to that is open technology,” he said.
For example, SAP Fioneer’s Engagement Hub is a tool for insurers to connect in an evolving ecosystem. With bi-directional communication, the Hub links a core insurance system with diverse digital channels, letting insurers craft tailored insurance solutions and adapt to market demands. The Cloud for Insurance cloud-native platform boasts fully managed services, ecosystem integration, and an intuitive user experience, allowing users to scale, innovate, and adapt quickly.
For more information on how insurers can embrace open technology and navigate the transformative changes in the industry, download the ‘Insurance Everywhere All at Once’ whitepaper from SAP Fioneer today.
READ MORE
- 3 Steps to Successfully Automate Copilot for Microsoft 365 Implementation
- Trustworthy AI – the Promise of Enterprise-Friendly Generative Machine Learning with Dell and NVIDIA
- Strategies for Democratizing GenAI
- The criticality of endpoint management in cybersecurity and operations
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications
