
Nvidia debuts a gaming chip with reduced speed in China to align with US restrictions on specific technology sales to the country.
Nvidia is supercharging the AI revolution with H200, its most powerful chip yet
- Nvidia said the H200 Tensor Core GPU has more memory capacity and bandwidth, speeding up its work with generative AI and HPC workloads.
- The Nvidia H200 is the first GPU to offer HBM3e — faster, larger memory to fuel the acceleration of Generative AI and LLMs.
- The H200 chips are set for 2Q24 release, and Nvidia said it would collaborate with “global system manufacturers and cloud service providers” for widespread availability.
It is almost a year since OpenAI launched ChatGPT, and the global demand for AI chips is growing more insatiable than ever. Today, most large tech firms focus all their attention on generative AI. It has never been better for the company that makes the most and highest-performance graphics processing units (GPUs), Nvidia Corp. After releasing dozens of chips to cater to the AI market that is growing at a seemingly exponential rate, the graphic chip giant teased its most powerful GPU yet–the H200.
The NVIDIA H200 Tensor Core GPU came at a time when Nvidia is striving to defend its dominant position in the AI computing space in the face of Intel, AMD, and a slew of chip startups and cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services trying to capture market share amid a boom in demand for chips driven by generative AI workloads.
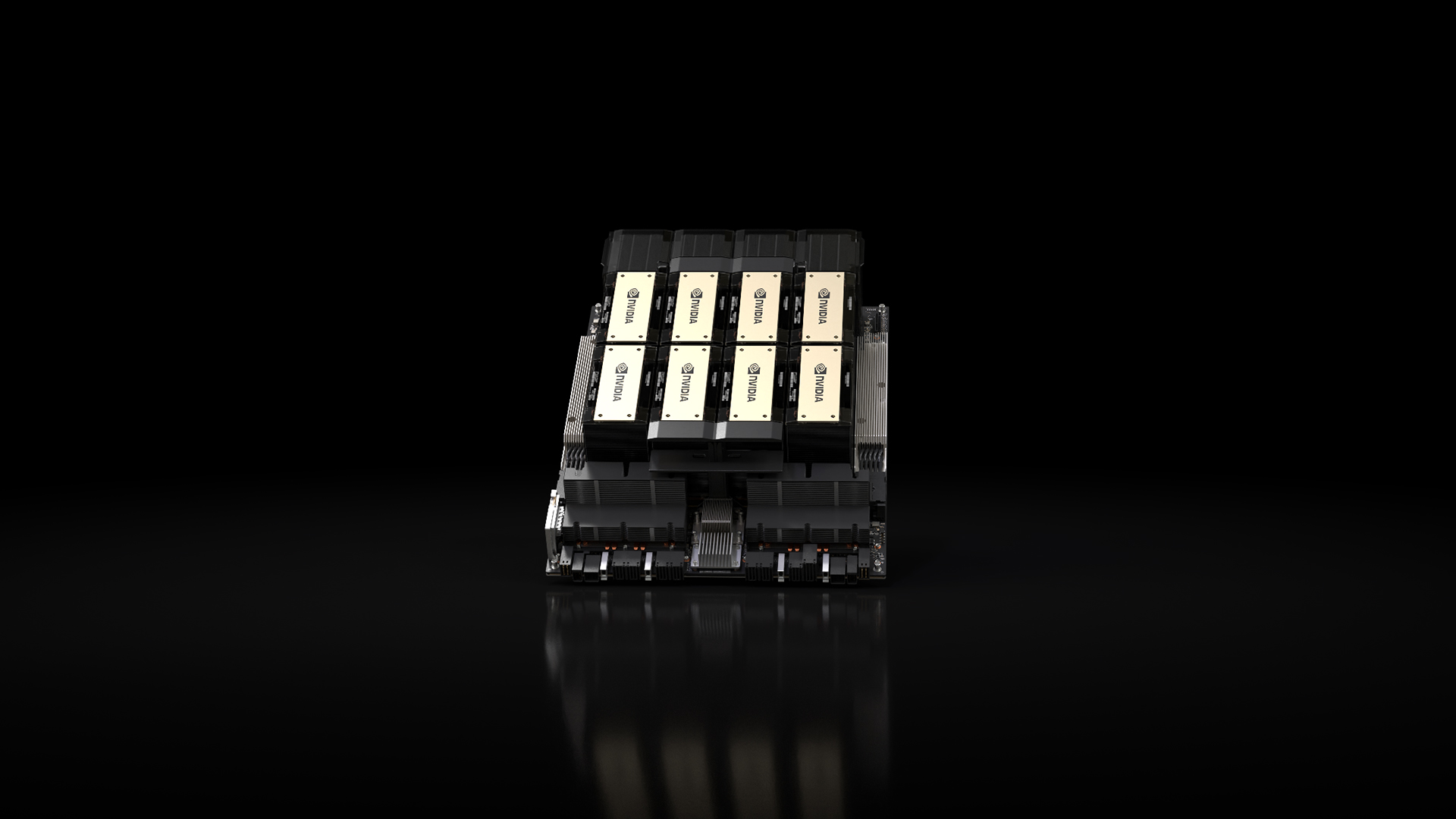
The NVIDIA H200 Tensor Core GPU. Source: Nvidia
To maintain its leadership in AI and high-performance computing (HPC) hardware, Nvidia unveiled early last month its plans to speed up the development of new GPU architectures. The idea is to get back to its one-year cadence for product introductions, according to its roadmap published for investors and further explained by SemiAnalysis. “Nvidia’s move to annual updates on AI GPUs is very significant and has many ramifications,” the report by SemiAnalysis reads.
And the start of it all would be the H200, which Nvidia had unveiled yesterday, utilizing the Hopper architecture to accelerate AI applications. It’s a follow-up of the H100 GPU, released last year and previously Nvidia’s most powerful AI GPU chip. In short, the H200 is now the most powerful AI chip Nvidia has in its portfolio.
Ian Buck, vice president of hyperscale and HPC at Nvidia, reckons that “With Nvidia H200, the industry’s leading end-to-end AI supercomputing platform, just got faster to solve some of the world’s most important challenges.” Generally, GPUs excel in AI applications due to their ability to execute numerous parallel matrix multiplications, a crucial operation for the functioning of neural networks.
They play a vital role in both the training phase of constructing an AI model and the subsequent “inference” stage, where users input data into the AI model, and it provides corresponding results. “To create intelligence with generative AI and HPC applications, vast amounts of data must be efficiently processed at high speed using large, fast GPU memory,” Buck noted.
Therefore, introducing H200 will lead to further performance leaps, including nearly doubling inference speed on Llama 2, a 70 billion-parameter LLM, compared to the H100. According to Nvidia, additional performance leadership and improvements with H200 are expected with future software updates.
Other details on Nvidia H200

TensorRT-LLM evaluation of the new H200 GPU achieves 11,819 tokens/s on Llama2-13B on a single GPU. H200 is up to 1.9x faster than H100. This performance is enabled by H200’s larger, faster HBM3e memory. Source: X
While the H200 seems mainly similar to the H100, the modifications to its memory represent a significant enhancement. The new GPU introduces an innovative and faster memory specification known as HBM3e. This elevates the GPU’s memory bandwidth to 4.8 terabytes per second, a notable increase from the H100’s 3.35 terabytes per second. It expands its total memory capacity to 141GB, up from the 80GB of its forerunner.
“The Nvidia H200 is the first GPU to offer HBM3e — faster, larger memory to fuel the acceleration of generative AI and large language models (LLMs) while advancing scientific computing for HPC workloads. With HBM3e, the NVIDIA H200 delivers 141GB of memory at 4.8 terabytes per second, nearly double the capacity and 2.4x more bandwidth compared with its predecessor, the NVIDIA A100,” the chip giant said.
To put into context, OpenAI has frequently mentioned facing a shortage of GPU resources, leading to performance slowdowns in ChatGPT. To maintain any level of service, the company resorts to rate limiting. In theory, incorporating the H200 could alleviate resource constraints for the current AI language models running ChatGPT, allowing them to cater to a more extensive customer base efficiently.
Nvidia also said it will make the H200 available in several form factors. This includes Nvidia HGX H200 server boards in four- and eight-way configurations, compatible with both hardware and software of HGX H100 systems. It will also be available in the Nvidia GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip, which combines a CPU and GPU into one package.
“With these options, H200 can be deployed in every type of data center, including on-premises, cloud, hybrid-cloud, and edge. NVIDIA’s global ecosystem of partner server makers — including ASRock Rack, ASUS, Dell Technologies, Eviden, GIGABYTE, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Ingrasys, Lenovo, QCT, Supermicro, Wistron, and Wiwynn — can update their existing systems with an H200,” Nvidia noted.
According to the US-based chip giant Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure will be among the first cloud service providers to deploy H200-based instances starting next year, in addition to CoreWeave, Lambda, and Vultr. At present, Nvidia is at the forefront of the AI GPU market.
However, major players such as AWS, Google, Microsoft, and traditional AI and HPC entities like AMD are actively preparing their next-generation processors for both training and inference. In response to this competitive landscape, Nvidia expedited its B100 and X100-based product timelines.
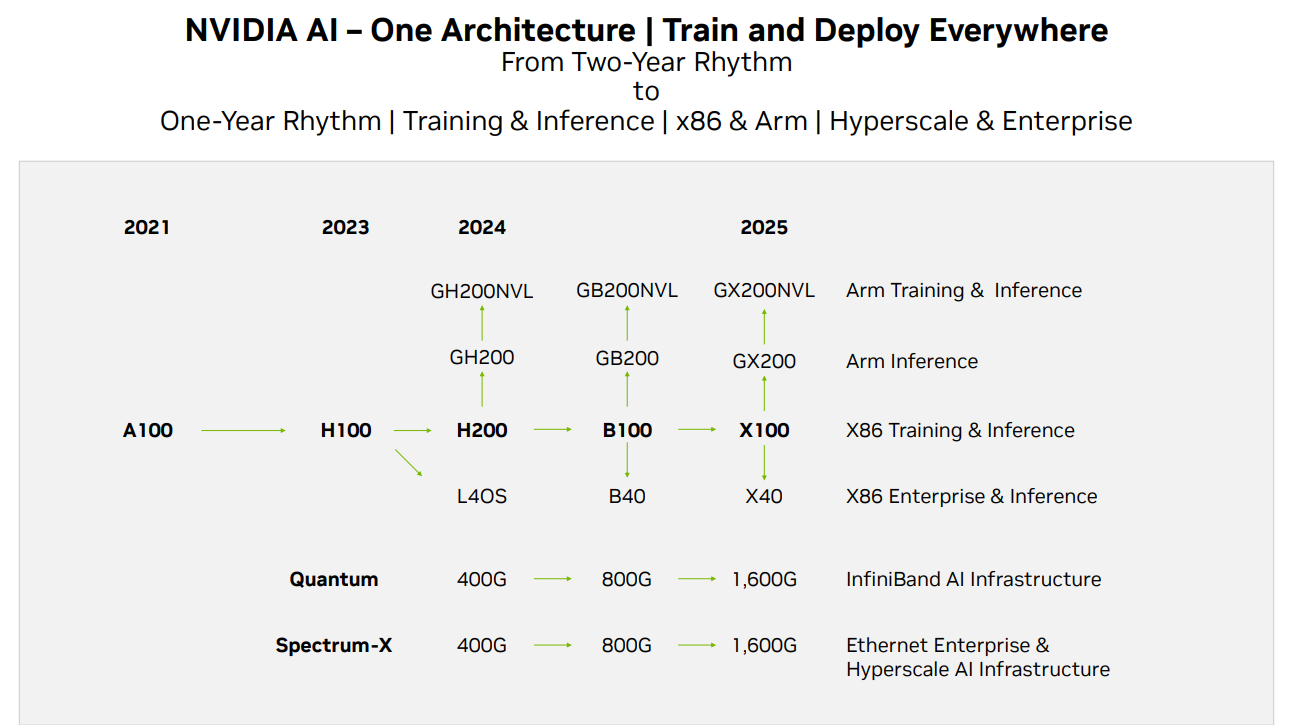
Nvidia plans to speed up development of new GPU architectures and essentially get back to its one-year cadence for product introductions, according to its roadmap published for investors. Source: Nvidia
READ MORE
- 3 Steps to Successfully Automate Copilot for Microsoft 365 Implementation
- Trustworthy AI – the Promise of Enterprise-Friendly Generative Machine Learning with Dell and NVIDIA
- Strategies for Democratizing GenAI
- The criticality of endpoint management in cybersecurity and operations
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications


